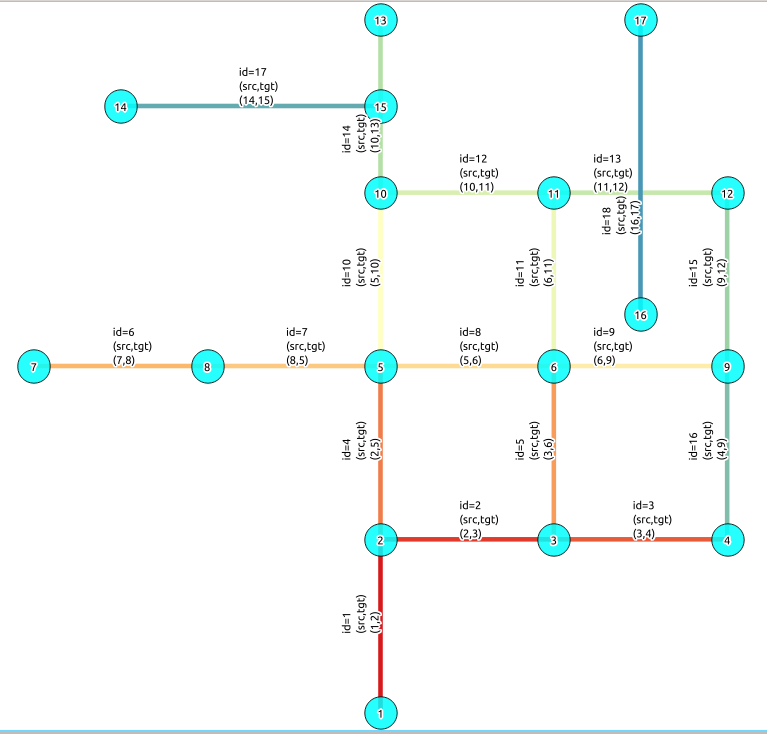
Datos Muestra¶
La documentación proporciona consultas de ejemplo muy simples basadas en una red muestra pequeña. Para ser capaz de ejecutar las consultas de la muestra, ejecute los siguientes comandos SQL para crear una tabla con el conjunto de datos de la red.
Crear tabla
CREATE TABLE edge_table (
id serial,
dir character varying,
source integer,
target integer,
cost double precision,
reverse_cost double precision,
x1 double precision,
y1 double precision,
x2 double precision,
y2 double precision,
the_geom geometry
);
Insertar los datos de la red
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1, 1, 2,0, 2,1);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES (-1, 1, 2,1, 3,1);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES (-1, 1, 3,1, 4,1);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1, 1, 2,1, 2,2);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1,-1, 3,1, 3,2);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1, 1, 0,2, 1,2);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1, 1, 1,2, 2,2);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1, 1, 2,2, 3,2);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1, 1, 3,2, 4,2);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1, 1, 2,2, 2,3);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1,-1, 3,2, 3,3);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1,-1, 2,3, 3,3);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1,-1, 3,3, 4,3);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1, 1, 2,3, 2,4);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1, 1, 4,2, 4,3);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1, 1, 4,1, 4,2);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1, 1, 0.5,3.5, 1.999999999999,3.5);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1, 1, 3.5,2.3, 3.5,4);
UPDATE edge_table SET the_geom = st_makeline(st_point(x1,y1),st_point(x2,y2)),
dir = CASE WHEN (cost>0 and reverse_cost>0) THEN 'B' -- both ways
WHEN (cost>0 and reverse_cost<0) THEN 'FT' -- direction of the LINESSTRING
WHEN (cost<0 and reverse_cost>0) THEN 'TF' -- reverse direction of the LINESTRING
ELSE '' END; -- unknown
Antes de probar la función de enrrutamiento utilice esta consulta para llenar las columnas de origen source y de destino target.
SELECT pgr_createTopology('edge_table',0.001);
Esta tabla se utiliza en algunos de nuestros ejemplos
CREATE TABLE vertex_table (
id serial,
x double precision,
y double precision
);
INSERT INTO vertex_table VALUES
(1,2,0), (2,2,1), (3,3,1), (4,4,1), (5,0,2), (6,1,2), (7,2,2),
(8,3,2), (9,4,2), (10,2,3), (11,3,3), (12,4,3), (13,2,4);
La red creada en edge_table