pgr_lineGraph — Transforms a given graph into its corresponding edge-based graph.
Warning
Experimental functions
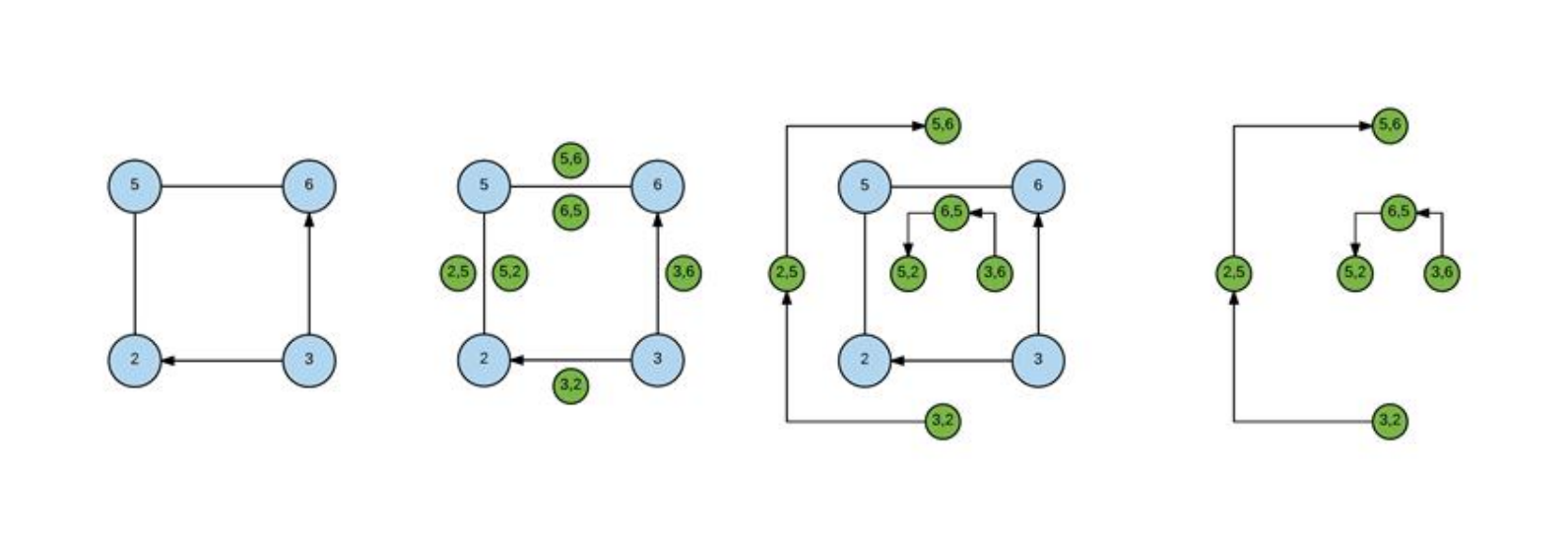
Given a graph G, its line graph L(G) is a graph such that:-
The following figures show a graph (left, with blue vertices) and its Line Graph (right, with green vertices).
pgr_lineGraph(edges_sql, directed)
RETURNS SET OF (seq, source, target, cost, reverse_cost)
OR EMPTY SET
pgr_lineGraph(edges_sql)
RETURNS SET OF (seq, source, target, cost, reverse_cost) or EMPTY SET
The minimal signature is for a directed graph:
| Example: |
|---|
SELECT * FROM pgr_lineGraph(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM edge_table'
);
seq | source | target | cost | reverse_cost
-----+--------+--------+------+--------------
1 | -18 | 18 | 1 | 1
2 | -17 | 17 | 1 | 1
3 | -16 | -3 | 1 | -1
4 | -16 | 16 | 1 | 1
5 | -15 | -9 | 1 | 1
6 | -15 | 15 | 1 | 1
7 | -14 | -10 | 1 | 1
8 | -14 | 12 | 1 | -1
9 | -14 | 14 | 1 | 1
10 | -10 | -7 | 1 | 1
11 | -10 | -4 | 1 | 1
12 | -10 | 8 | 1 | 1
13 | -10 | 10 | 1 | 1
14 | -9 | -8 | 1 | 1
15 | -9 | 9 | 1 | 1
16 | -9 | 11 | 1 | -1
17 | -8 | -7 | 1 | 1
18 | -8 | -4 | 1 | 1
19 | -8 | 8 | 1 | 1
20 | -7 | -6 | 1 | 1
21 | -6 | 6 | 1 | 1
22 | -4 | -1 | 1 | 1
23 | -4 | 4 | 1 | 1
24 | -3 | -2 | 1 | -1
25 | -3 | 5 | 1 | -1
26 | -2 | -1 | 1 | -1
27 | -2 | 4 | 1 | -1
28 | -1 | 1 | 1 | 1
29 | 5 | -8 | 1 | -1
30 | 5 | 9 | 1 | -1
31 | 5 | 11 | 1 | -1
32 | 7 | -7 | 1 | 1
33 | 7 | -4 | 1 | 1
34 | 8 | 11 | 1 | -1
35 | 10 | 12 | 1 | -1
36 | 11 | 13 | 1 | -1
37 | 12 | 13 | 1 | -1
38 | 13 | -15 | 1 | -1
39 | 16 | -9 | 1 | 1
40 | 16 | 15 | 1 | 1
(40 rows)
pgr_lineGraph(edges_sql, directed);
RETURNS SET OF (seq, source, target, cost, reverse_cost) or EMPTY SET
directed flag is missing or is set to true.directed flag is set to false.| Example: |
|---|
SELECT * FROM pgr_lineGraph(
'SELECT id, source, target, cost, reverse_cost FROM edge_table',
FALSE
);
seq | source | target | cost | reverse_cost
-----+--------+--------+------+--------------
1 | -3 | -2 | 1 | -1
2 | -3 | 5 | 1 | -1
3 | -2 | 4 | 1 | -1
4 | 1 | 4 | 1 | -1
5 | 4 | 8 | 1 | -1
6 | 4 | 10 | 1 | -1
7 | 5 | 9 | 1 | -1
8 | 5 | 11 | 1 | -1
9 | 6 | 7 | 1 | -1
10 | 7 | 8 | 1 | -1
11 | 7 | 10 | 1 | -1
12 | 8 | 9 | 1 | -1
13 | 8 | 11 | 1 | -1
14 | 9 | 15 | 1 | -1
15 | 10 | 12 | 1 | -1
16 | 10 | 14 | 1 | -1
17 | 11 | 13 | 1 | -1
18 | 12 | 13 | 1 | -1
19 | 16 | 15 | 1 | -1
(19 rows)
| edges_sql: | an SQL query, which should return a set of rows with the following columns: |
|---|
| Column | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| id | ANY-INTEGER |
Identifier of the edge. | |
| source | ANY-INTEGER |
Identifier of the first end point vertex of the edge. | |
| target | ANY-INTEGER |
Identifier of the second end point vertex of the edge. | |
| cost | ANY-NUMERICAL |
Weight of the edge (source, target)
|
|
| reverse_cost | ANY-NUMERICAL |
-1 | Weight of the edge (target, source),
|
Where:
| ANY-INTEGER: | SMALLINT, INTEGER, BIGINT |
|---|---|
| ANY-NUMERICAL: | SMALLINT, INTEGER, BIGINT, REAL, FLOAT |
| Column | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| edges_sql | TEXT |
SQL query as described above. |
| directed | BOOLEAN |
|
RETURNS SETOF (seq, source, target, cost, reverse_cost)
| Column | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| seq | INTEGER |
Sequential value starting from 1. |
| source | BIGINT |
Identifier of the source vertex of the current edge id.
|
| target | BIGINT |
Identifier of the target vertex of the current edge id.
|
| cost | FLOAT |
Weight of the edge (source, target).
|
| reverse_cost | FLOAT |
Weight of the edge (target, source).
|
Indices and tables