Unsupported versions:2.6 2.5 2.4 2.3 2.2 2.1 2.0
pgr_createTopology¶
pgr_createTopology — Builds a network topology based on the geometry
information.
Availability
Version 2.0.0
Renamed from version 1.x
Official function
Description¶
The function returns:
OKafter the network topology has been built and the vertices table created.FAILwhen the network topology was not built due to an error.
Signatures¶
[the_geom, id, source, target, rows_where, clean]VARCHARParameters¶
The topology creation function accepts the following parameters:
- edge_table:
textNetwork table name. (may contain the schema name AS well)- tolerance:
float8Snapping tolerance of disconnected edges. (in projection unit)- the_geom:
textGeometry column name of the network table. Default value isthe_geom.- id:
textPrimary key column name of the network table. Default value isid.- source:
textSource column name of the network table. Default value issource.- target:
textTarget column name of the network table. Default value istarget.- rows_where:
textCondition to SELECT a subset or rows. Default value istrueto indicate all rows that wheresourceortargethave a null value, otherwise the condition is used.- clean:
booleanClean any previous topology. Default value isfalse.
Warning
The edge_table will be affected
The
sourcecolumn values will change.The
targetcolumn values will change.An index will be created, if it doesn’t exists, to speed up the process to the following columns:
idthe_geomsourcetarget
The function returns:
OKafter the network topology has been built.Creates a vertices table: <edge_table>_vertices_pgr.
Fills
idandthe_geomcolumns of the vertices table.Fills the source and target columns of the edge table referencing the
idof the vertices table.
FAILwhen the network topology was not built due to an error:A required column of the Network table is not found or is not of the appropriate type.
The condition is not well formed.
The names of source , target or id are the same.
The SRID of the geometry could not be determined.
The Vertices Table
The vertices table is a requirement of the pgr_analyzeGraph and the pgr_analyzeOneWay functions.
The structure of the vertices table is:
- id:
bigintIdentifier of the vertex.- cnt:
integerNumber of vertices in the edge_table that reference this vertex. See pgr_analyzeGraph.- chk:
integerIndicator that the vertex might have a problem. See pgr_analyzeGraph.- ein:
integerNumber of vertices in the edge_table that reference this vertex AS incoming. See pgr_analyzeOneWay.- eout:
integerNumber of vertices in the edge_table that reference this vertex AS outgoing. See pgr_analyzeOneWay.- the_geom:
geometryPoint geometry of the vertex.
Usage when the edge table’s columns MATCH the default values:¶
The simplest way to use pgr_createTopology is:
SELECT pgr_createTopology('edges', 0.001, 'geom');
NOTICE: PROCESSING:
NOTICE: pgr_createTopology('edges', 0.001, 'geom', 'id', 'source', 'target', rows_where := 'true', clean := f)
NOTICE: Performing checks, please wait .....
NOTICE: Creating Topology, Please wait...
NOTICE: -------------> TOPOLOGY CREATED FOR 18 edges
NOTICE: Rows with NULL geometry or NULL id: 0
NOTICE: Vertices table for table public.edges is: public.edges_vertices_pgr
NOTICE: ----------------------------------------------
pgr_createtopology
--------------------
OK
(1 row)
When the arguments are given in the order described:
We get the same result AS the simplest way to use the function.
SELECT pgr_createTopology('edges', 0.001,
'geom', 'id', 'source', 'target');
NOTICE: PROCESSING:
NOTICE: pgr_createTopology('edges', 0.001, 'geom', 'id', 'source', 'target', rows_where := 'true', clean := f)
NOTICE: Performing checks, please wait .....
NOTICE: Creating Topology, Please wait...
NOTICE: -------------> TOPOLOGY CREATED FOR 18 edges
NOTICE: Rows with NULL geometry or NULL id: 0
NOTICE: Vertices table for table public.edges is: public.edges_vertices_pgr
NOTICE: ----------------------------------------------
pgr_createtopology
--------------------
OK
(1 row)
Warning
An error would occur when the arguments are not given in the appropriate
order: In this example, the column id of the table ege_table is
passed to the function as the geometry column, and the geometry column
the_geom is passed to the function as the id column.
SELECT pgr_createTopology('edges', 0.001,
'id', 'geom');
NOTICE: PROCESSING:
NOTICE: pgr_createTopology('edges', 0.001, 'id', 'geom', 'source', 'target', rows_where := 'true', clean := f)
NOTICE: Performing checks, please wait .....
NOTICE: ----> PGR ERROR in pgr_createTopology: Wrong type of Column id:geom
HINT: ----> Expected type of geom is integer,smallint or bigint but USER-DEFINED was found
NOTICE: Unexpected error raise_exception
pgr_createtopology
--------------------
FAIL
(1 row)
When using the named notation
Parameters defined with a default value can be omitted, as long as the value matches the default And The order of the parameters would not matter.
SELECT pgr_createTopology('edges', 0.001,
the_geom:='geom', id:='id', source:='source', target:='target');
pgr_createtopology
--------------------
OK
(1 row)
SELECT pgr_createTopology('edges', 0.001,
source:='source', id:='id', target:='target', the_geom:='geom');
pgr_createtopology
--------------------
OK
(1 row)
SELECT pgr_createTopology('edges', 0.001, 'geom', source:='source');
pgr_createtopology
--------------------
OK
(1 row)
Selecting rows using rows_where parameter
Selecting rows based on the id.
SELECT pgr_createTopology('edges', 0.001, 'geom', rows_where:='id < 10');
pgr_createtopology
--------------------
OK
(1 row)
Selecting the rows where the geometry is near the geometry of row with id =
5.
SELECT pgr_createTopology('edges', 0.001, 'geom',
rows_where:='geom && (SELECT st_buffer(geom, 0.05) FROM edges WHERE id=5)');
pgr_createtopology
--------------------
OK
(1 row)
Selecting the rows where the geometry is near the geometry of the row with
gid =100 of the table othertable.
CREATE TABLE otherTable AS (SELECT 100 AS gid, st_point(2.5, 2.5) AS other_geom);
SELECT 1
SELECT pgr_createTopology('edges', 0.001, 'geom',
rows_where:='geom && (SELECT st_buffer(other_geom, 1) FROM otherTable WHERE gid=100)');
pgr_createtopology
--------------------
OK
(1 row)
Usage when the edge table’s columns DO NOT MATCH the default values:¶
For the following table
CREATE TABLE mytable AS (SELECT id AS gid, geom AS mygeom, source AS src , target AS tgt FROM edges) ;
SELECT 18
Using positional notation:
The arguments need to be given in the order described in the parameters.
Note that this example uses clean flag. So it recreates the whole vertices table.
SELECT pgr_createTopology('mytable', 0.001, 'mygeom', 'gid', 'src', 'tgt', clean := TRUE);
pgr_createtopology
--------------------
OK
(1 row)
Warning
An error would occur when the arguments are not given in the appropiriate
order: In this example, the column gid of the table mytable is passed
to the function AS the geometry column, and the geometry column mygeom is
passed to the function AS the id column.
SELECT pgr_createTopology('mytable', 0.001, 'gid', 'mygeom', 'src', 'tgt'); NOTICE: PROCESSING: NOTICE: pgr_createTopology('mytable', 0.001, 'gid', 'mygeom', 'src', 'tgt', rows_where := 'true', clean := f) NOTICE: Performing checks, please wait ..... NOTICE: ----> PGR ERROR in pgr_createTopology: Wrong type of Column id:mygeom HINT: ----> Expected type of mygeom is integer,smallint or bigint but USER-DEFINED was found NOTICE: Unexpected error raise_exception pgr_createtopology -------------------- FAIL (1 row)
When using the named notation
In this scenario omitting a parameter would create an error because the default values for the column names do not match the column names of the table. The order of the parameters do not matter:
SELECT pgr_createTopology('mytable', 0.001, the_geom:='mygeom', id:='gid', source:='src', target:='tgt');
pgr_createtopology
--------------------
OK
(1 row)
SELECT pgr_createTopology('mytable', 0.001, source:='src', id:='gid', target:='tgt', the_geom:='mygeom');
pgr_createtopology
--------------------
OK
(1 row)
Selecting rows using rows_where parameter
Based on id:
SELECT pgr_createTopology('mytable', 0.001, 'mygeom', 'gid', 'src', 'tgt', rows_where:='gid < 10');
pgr_createtopology
--------------------
OK
(1 row)
SELECT pgr_createTopology('mytable', 0.001, source:='src', id:='gid', target:='tgt', the_geom:='mygeom', rows_where:='gid < 10');
pgr_createtopology
--------------------
OK
(1 row)
SELECT pgr_createTopology('mytable', 0.001, 'mygeom', 'gid', 'src', 'tgt',
rows_where:='mygeom && (SELECT st_buffer(mygeom, 1) FROM mytable WHERE gid=5)');
pgr_createtopology
--------------------
OK
(1 row)
SELECT pgr_createTopology('mytable', 0.001, source:='src', id:='gid', target:='tgt', the_geom:='mygeom',
rows_where:='mygeom && (SELECT st_buffer(mygeom, 1) FROM mytable WHERE gid=5)');
pgr_createtopology
--------------------
OK
(1 row)
Selecting the rows where the geometry is near the geometry of the row with
gid =100 of the table othertable.
SELECT pgr_createTopology('mytable', 0.001, 'mygeom', 'gid', 'src', 'tgt',
rows_where:='mygeom && (SELECT st_buffer(other_geom, 1) FROM otherTable WHERE gid=100)');
pgr_createtopology
--------------------
OK
(1 row)
SELECT pgr_createTopology('mytable', 0.001, source:='src', id:='gid', target:='tgt', the_geom:='mygeom',
rows_where:='mygeom && (SELECT st_buffer(other_geom, 1) FROM otherTable WHERE gid=100)');
pgr_createtopology
--------------------
OK
(1 row)
Additional Examples¶
Create a routing topology¶
An alternate method to create a routing topology use pgr_extractVertices – Proposed
Make sure the database does not have the vertices_table¶
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS vertices_table;
NOTICE: table "vertices_table" does not exist, skipping
DROP TABLE
Clean up the columns of the routing topology to be created¶
UPDATE edges
SET source = NULL, target = NULL,
x1 = NULL, y1 = NULL,
x2 = NULL, y2 = NULL;
UPDATE 18
Create the vertices table¶
When the
LINESTRINGhas a SRID then usegeom::geometry(POINT, <SRID>)For big edge tables that are been prepared,
Create it as
UNLOGGEDandAfter the table is created
ALTER TABLE .. SET LOGGED
SELECT * INTO vertices_table
FROM pgr_extractVertices('SELECT id, geom FROM edges ORDER BY id');
SELECT 17
Inspect the vertices table¶
SELECT *
FROM vertices_table;
id | in_edges | out_edges | x | y | geom
----+----------+-----------+----------------+-----+--------------------------------------------
1 | | {6} | 0 | 2 | 010100000000000000000000000000000000000040
2 | | {17} | 0.5 | 3.5 | 0101000000000000000000E03F0000000000000C40
3 | {6} | {7} | 1 | 2 | 0101000000000000000000F03F0000000000000040
4 | {17} | | 1.999999999999 | 3.5 | 010100000068EEFFFFFFFFFF3F0000000000000C40
5 | | {1} | 2 | 0 | 010100000000000000000000400000000000000000
6 | {1} | {2,4} | 2 | 1 | 01010000000000000000000040000000000000F03F
7 | {4,7} | {8,10} | 2 | 2 | 010100000000000000000000400000000000000040
8 | {10} | {12,14} | 2 | 3 | 010100000000000000000000400000000000000840
9 | {14} | | 2 | 4 | 010100000000000000000000400000000000001040
10 | {2} | {3,5} | 3 | 1 | 01010000000000000000000840000000000000F03F
11 | {5,8} | {9,11} | 3 | 2 | 010100000000000000000008400000000000000040
12 | {11,12} | {13} | 3 | 3 | 010100000000000000000008400000000000000840
13 | | {18} | 3.5 | 2.3 | 01010000000000000000000C406666666666660240
14 | {18} | | 3.5 | 4 | 01010000000000000000000C400000000000001040
15 | {3} | {16} | 4 | 1 | 01010000000000000000001040000000000000F03F
16 | {9,16} | {15} | 4 | 2 | 010100000000000000000010400000000000000040
17 | {13,15} | | 4 | 3 | 010100000000000000000010400000000000000840
(17 rows)
Create the routing topology on the edge table¶
Updating the source information
WITH
out_going AS (
SELECT id AS vid, unnest(out_edges) AS eid, x, y
FROM vertices_table
)
UPDATE edges
SET source = vid, x1 = x, y1 = y
FROM out_going WHERE id = eid;
UPDATE 18
Updating the target information
WITH
in_coming AS (
SELECT id AS vid, unnest(in_edges) AS eid, x, y
FROM vertices_table
)
UPDATE edges
SET target = vid, x2 = x, y2 = y
FROM in_coming WHERE id = eid;
UPDATE 18
Inspect the routing topology¶
SELECT id, source, target, x1, y1, x2, y2
FROM edges ORDER BY id;
id | source | target | x1 | y1 | x2 | y2
----+--------+--------+-----+-----+----------------+-----
1 | 5 | 6 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 1
2 | 6 | 10 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 1
3 | 10 | 15 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 1
4 | 6 | 7 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2
5 | 10 | 11 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2
6 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 2
7 | 3 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2
8 | 7 | 11 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2
9 | 11 | 16 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 2
10 | 7 | 8 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3
11 | 11 | 12 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3
12 | 8 | 12 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3
13 | 12 | 17 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3
14 | 8 | 9 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 4
15 | 16 | 17 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 3
16 | 15 | 16 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 2
17 | 2 | 4 | 0.5 | 3.5 | 1.999999999999 | 3.5
18 | 13 | 14 | 3.5 | 2.3 | 3.5 | 4
(18 rows)
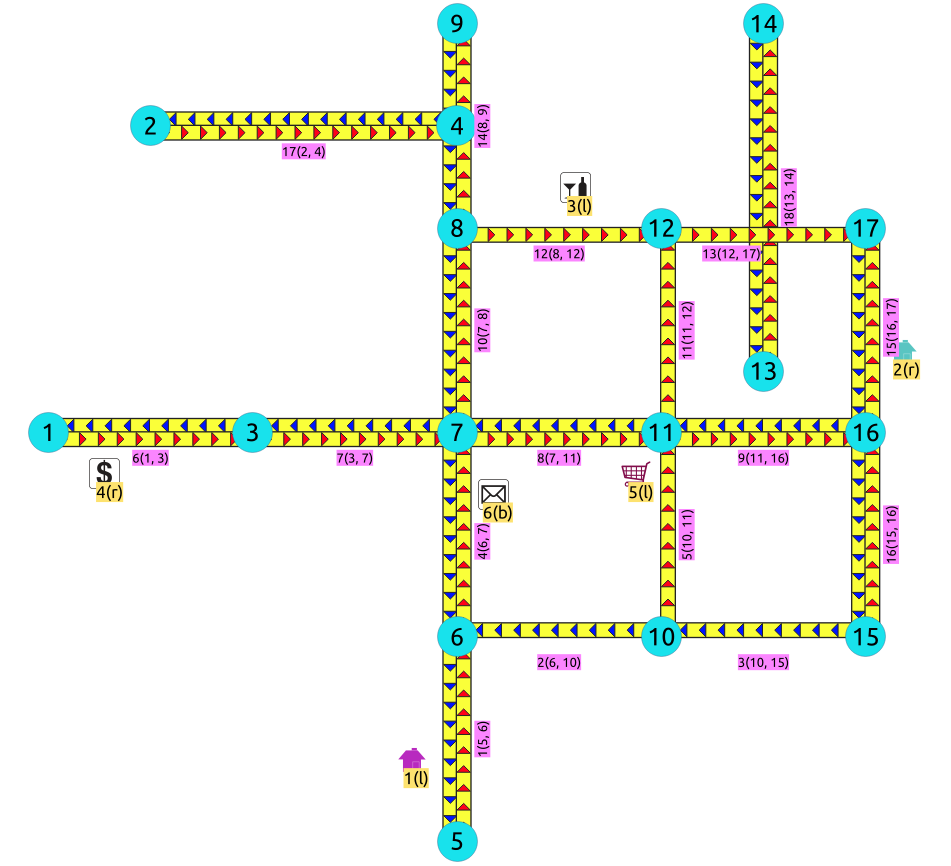
Generated topology¶
With full output¶
This example start a clean topology, with 5 edges, and then its incremented to the rest of the edges.
SELECT pgr_createTopology('edges', 0.001, 'geom', rows_where:='id < 6', clean := true);
NOTICE: PROCESSING:
NOTICE: pgr_createTopology('edges', 0.001, 'geom', 'id', 'source', 'target', rows_where := 'id < 6', clean := t)
NOTICE: Performing checks, please wait .....
NOTICE: Creating Topology, Please wait...
NOTICE: -------------> TOPOLOGY CREATED FOR 5 edges
NOTICE: Rows with NULL geometry or NULL id: 0
NOTICE: Vertices table for table public.edges is: public.edges_vertices_pgr
NOTICE: ----------------------------------------------
pgr_createtopology
--------------------
OK
(1 row)
SELECT pgr_createTopology('edges', 0.001, 'geom');
NOTICE: PROCESSING:
NOTICE: pgr_createTopology('edges', 0.001, 'geom', 'id', 'source', 'target', rows_where := 'true', clean := f)
NOTICE: Performing checks, please wait .....
NOTICE: Creating Topology, Please wait...
NOTICE: -------------> TOPOLOGY CREATED FOR 13 edges
NOTICE: Rows with NULL geometry or NULL id: 0
NOTICE: Vertices table for table public.edges is: public.edges_vertices_pgr
NOTICE: ----------------------------------------------
pgr_createtopology
--------------------
OK
(1 row)
The example uses the Sample Data network.
See Also¶
Indices and tables
