Unsupported versions:2.6 2.5 2.4 2.3 2.2 2.1 2.0
Sample Data¶
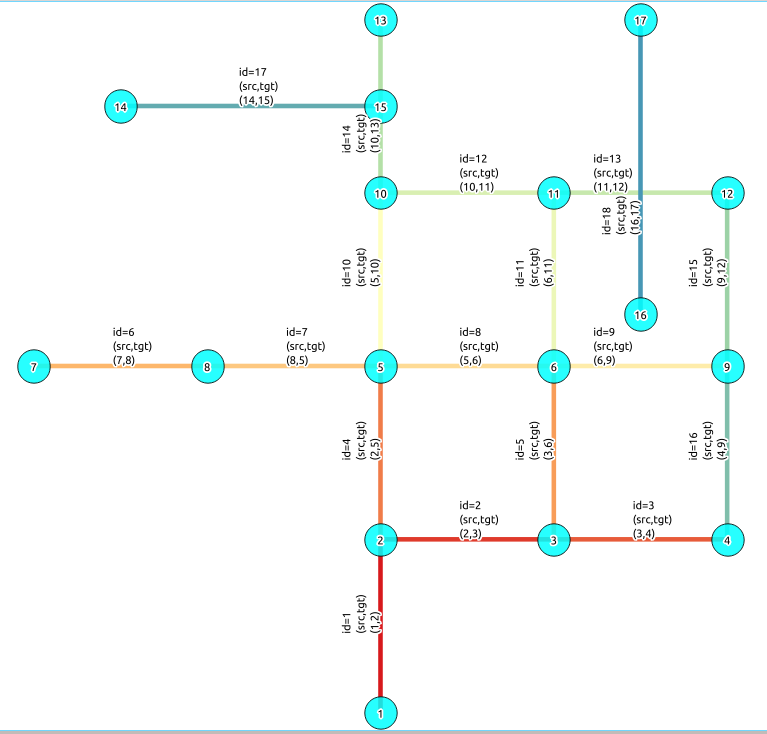
The documentation provides very simple example queries based on a small sample network. To be able to execute the sample queries, run the following SQL commands to create a table with a small network data set.
Create table
CREATE TABLE edge_table (
id serial,
dir character varying,
source integer,
target integer,
cost double precision,
reverse_cost double precision,
x1 double precision,
y1 double precision,
x2 double precision,
y2 double precision,
the_geom geometry
);
Insert network data
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1, 1, 2,0, 2,1);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES (-1, 1, 2,1, 3,1);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES (-1, 1, 3,1, 4,1);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1, 1, 2,1, 2,2);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1,-1, 3,1, 3,2);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1, 1, 0,2, 1,2);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1, 1, 1,2, 2,2);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1, 1, 2,2, 3,2);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1, 1, 3,2, 4,2);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1, 1, 2,2, 2,3);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1,-1, 3,2, 3,3);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1,-1, 2,3, 3,3);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1,-1, 3,3, 4,3);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1, 1, 2,3, 2,4);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1, 1, 4,2, 4,3);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1, 1, 4,1, 4,2);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1, 1, 0.5,3.5, 1.999999999999,3.5);
INSERT INTO edge_table (cost,reverse_cost,x1,y1,x2,y2) VALUES ( 1, 1, 3.5,2.3, 3.5,4);
UPDATE edge_table SET the_geom = st_makeline(st_point(x1,y1),st_point(x2,y2)),
dir = CASE WHEN (cost>0 and reverse_cost>0) THEN 'B' -- both ways
WHEN (cost>0 and reverse_cost<0) THEN 'FT' -- direction of the LINESSTRING
WHEN (cost<0 and reverse_cost>0) THEN 'TF' -- reverse direction of the LINESTRING
ELSE '' END; -- unknown
Before you test a routing function use this query to fill the source and target columns.
SELECT pgr_createTopology('edge_table',0.001);
This table is used in some of our examples
CREATE TABLE vertex_table (
id serial,
x double precision,
y double precision
);
INSERT INTO vertex_table VALUES
(1,2,0), (2,2,1), (3,3,1), (4,4,1), (5,0,2), (6,1,2), (7,2,2),
(8,3,2), (9,4,2), (10,2,3), (11,3,3), (12,4,3), (13,2,4);
The network created in edge_table